Already have your UTI Test Kit?
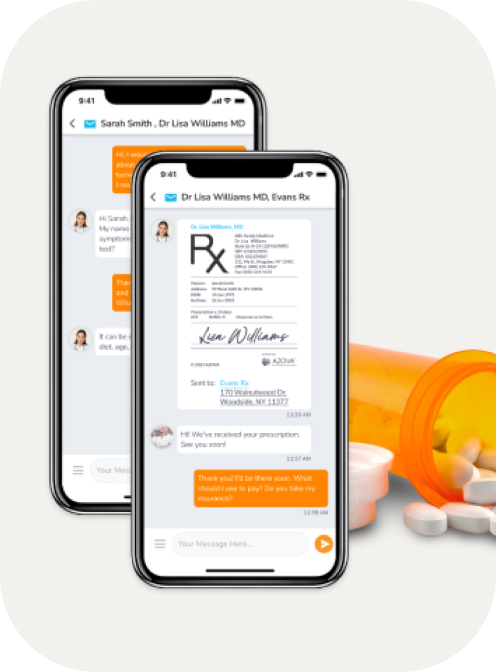
Get a Virtual Care visit for your urinary tract infection now
Solve your urinary tract infection today with an online Virtual Care visit with a board-certified provider. Get prescriptions, when necessary.


About the test kit
This test kit will check for urinary Leukocytes (white blood cells) and Nitrite, two markers that are seen in a urinary tract infection. If your test is positive, simply scan the QR code in this box and get a telemedicine visit at no additional charge. Your visit will be a secure messaging, telephone, or video visit based upon what is allowed in your state. If indicated, your provider will also send in a prescription for you.
8.1
Over 8.1 million doctor visits
occur annually due to UTIs.
30%
Up to 30% of sepsis cases are
caused by UTIs.
3%
Around 3% of UTIs result in a
kidney infection.
What you get
UTI learning library
Signs and symptoms
Location of UTI and their symptoms
Overview/Introduction
The urinary tract is the system of organs and tubes responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine from the body. The urinary tract consists of the following organs and structures:
- Kidneys – These are two bean-shaped organs located in the back of the abdomen that filter waste products and excess water from the blood to produce urine.
- Ureters – These are two narrow tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder and transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder – This is a muscular sac located in the lower abdomen that stores urine until it is eliminated from the body.
- Urethra – This is a tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) can occur anywhere in the urinary tract. Signs and symptoms of UTI may differ depending on the location and severity of the infection.
Discussion
The types of UTI based on location and the symptoms they exhibit are:
- Urethritis. This is an inflammation of the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. Common symptoms include:
Pain or burning during urination
Frequent or urgent need to urinate
Discharge from the penis in men
Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Itching or irritation in the urethral opening in men or women
In some cases, people with urethritis may also experience pain during sexual intercourse. - Cystitis. This type of UTI occurs in the bladder. The symptoms of cystitis include:
Pain or burning during urination
Frequent or urgent need to urinate
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area - Pyelonephritis. This is a type of UTI that involves the kidneys. Symptoms include:
Fever, often with chills and sweating. This usually distinguishes cystitis from pyelonephritis.Frequent or urgent need to urinate
Pain or tenderness in the back or side (flank pain)
Nausea and vomiting
Symptoms of urethritis/cystitis may also be present
Other important information
UTI may also be classified as lower UTI (urethritis and cystitis) and as upper UTI (pyelonephritis). Lower UTIs are generally more common and simpler to treat than upper UTIs.
Conclusion/Summary
Symptoms of UTI may vary from person to person and also depending on the location of the infection in the urinary tract. All types of UTI need to be treated, but some infections may be more severe than others. Pyelonephritis is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention, as untreated infections can lead to complications such as kidney damage and sepsis. If you have any of the symptoms of UTI, consult with your doctor for the appropriate management.
UTI Symptoms vs other conditions: How to tell the difference?
Overview/Introduction
The symptoms of UTI like burning sensation when urinating, frequent urge to urinate and pelvic pain may be similar to other conditions like yeast infections and sexually transmitted illnesses (STIs). STIs can be more serious than your typical UTI and they are more likely to spread from one person to another. How can you tell the difference between UTI symptoms and other conditions?
Bladder Infection vs Other UTIs
A UTI is an infection of any section of the urinary tract, which includes the urethra, kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It could be challenging to determine which section of the urinary system is infected. Common symptoms include pain or burning sensation during urination, pain in the pelvic area, blood in the urine, or waking at night to urinate. The signs of a UTI in other sections of the urinary system are similar to those of a bladder infection, often known as cystitis. Bladder pain is not a symptom of an infection in the urethra, although it may produce pain and burning during peeing as well as discharge from the urethra. Serious signs of an infection that has reached the kidneys is known as pyelonephritis. A person with a kidney infection could also have fever, chills, nausea, and back discomfort.
Similarities and Differences between UTIs and Yeast Infections
Yeast infections and UTIs are two distinct infections. Despite being in the same general area, their symptoms are different. UTI symptoms usually present with symptoms associated with urination. They could make you feel like you need to urinate more often or give you a burning feeling when you do. In addition to difficulty during urination, a yeast infection can cause pain and itching in the affected area. A thick, milky discharge is another usual symptom of vaginal yeast infections.
Similarities and Differences between UTIs and STIs
UTI’s and STIs share similar symptoms and may be difficult to distinguish. Despite the fact that many STIs are asymptomatic (present with no symptoms), there are a few differences that could help you determine if your disease is in your urinary tract or reproductive organs. STIs are frequently brought on by gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma. They occasionally result in urethral discharge and can make urinating unpleasant. Both UTI and STI may present with urinary symptoms, unusual discharge and cloudy urine. Symptoms that point more towards STI include pain during intercourse, vaginal rash or rash in the genital area, and vaginal bleeding.
Conclusion/Summary
If any of your symptoms increase, worsen or change from the normal UTI symptoms, it might be an STI or another infection instead. If symptoms start to include ones like discharge or smell, it’s far more likely to be one of the most common STIs. Visit your doctor if you experience any symptoms that could indicate something other than a urinary tract infection.
How UTI can affect Kidney function: Signs and Symptoms to Watch out for
Overview/Introduction
If left untreated, UTIs might continue to move higher into your kidneys. A kidney infection can lead to serious problems, including kidney damage or a life threatening condition called sepsis. In other words, kidney infections typically occur from the untreated progression of a less serious UTI.
Discussion
When dangerous germs from an infection of the urinary system (UTI) make their way to your kidneys, it causes a kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis.
Kidneys aren’t typically affected by UTIs. Your urethra and bladder are the only parts of your lower urinary tract that are affected. Nevertheless, occasionally, an infection that starts there spreads to your upper urinary tract and impacts one or both of your kidneys. It’s crucial to get medical attention if you experience any of the signs of a UTI or bladder infection (also known as cystitis), including pain when urinating, foul-smelling urine, groin pain, or stained urine.
Pay attention to symptoms that may show your infection has spread to your kidneys and may suggest a more serious kidney problem or dysfunction. These are the following:
- fever
- chills
- localized discomfort in the side or lower back
- nausea or vomiting
- not peeing or barely peeing
- mental confusion
- difficulty in breathing
- loss of appetite
- low blood pressure
- fast heartbeat
Serious kidney infections may necessitate hospitalization of the patient. You might be given fluids and antibiotics intravenously in this situation. It’s important that you visit a doctor if you experience any UTI symptoms. A potentially dangerous kidney infection can be avoided by receiving a correct medical diagnosis and beginning antibiotic therapy.
Other Important Information
Kidney infections can be highly painful and require quick evaluation and treatment. If your infection isn’t treated right away, it could cause irreversible kidney damage or spread to your bloodstream, which could cause sepsis (infection in the bloodstream) and compromise other essential organs.
Conclusion/Summary
Infection that is not treated can harm the kidneys and cause long-term issues. Renal dysfunction, or kidney failure are uncommon outcomes of kidney infections. Sepsis is a dangerous condition that can develop if a kidney infection gets into the bloodstream. Speak to a healthcare provider if you experience signs of a kidney infection. Pay attention to your doctor’s instructions for how to care for yourself at home and how to take any recommended medications.
The Danger of Ignoring UTI Symptoms
Overview/Introduction
UTIs are one of the most prevalent diseases that affect people all over the world and considered as a serious public health concern. UTI affects almost 150 million individuals globally each year. In 2007, an estimated 10.5 million office visits for UTI symptoms were reported in the United States (representing 0.9 percent of total ambulatory visits) and 2-3 million emergency room visits were recorded.
Women are approximately eight times more likely to develop a UTI than men. UTIs may present with symptoms including pain with urination, blood in the urine, fever and chills, and flank pain if the kidney is also infected. UTIs can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
A person is more likely to have UTI if he/she have symptoms such as:
- Painful or burning sensation upon urination
- Strong and persistent urge to urinate
- Increased urinary frequency with little volumes of urine
- Lower abdominal, lower back, flank, pelvic pain or pressure
- Pink, red, or brown urine
- Bloody or cloudy urine
- Strange-smelling urine
- Fever or chills
Discussion
If a person suspects that he/she has a UTI, immediate medical assistance should be done. A UTI, if left untreated, can progress from lower to the upper urinary tract and develop kidney infection known as pyelonephritis. A UTI involving the kidneys might cause the following symptoms:
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain, discomfort and/or burning sensation upon urination
- Flank and/or back pain that does not go away when changing positions
Kidney infection can be treated with oral antibiotics. In some people with complicated infection and/or concomitant disease and health condition, patients can be admitted in the hospital and can be given intravenous antibiotics and fluids. However, if kidney infection is left untreated, a person will develop sepsis or severe blood infection, which is a life-threatening condition. Sepsis can be can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Decreased in blood pressure
- Increased in respiratory rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Erratic or rapid heart rate
- Sudden variations in body temperature
- Loss of consciousness and/or change in mental status
- Fever and chills
Sepsis management includes hospitalization, intravenous antibiotic administration, and intravenous fluid therapy.
Conclusion/Summary
Untreated urinary tract infections increase the chance of recurrence or possibly therapeutic failure. The urinary tract infection has the potential to spread to other organs, form an abscess, or develop to sepsis. Other complications from untreated UTI are kidney damage or injury, urethral narrowing or stricture, low birth weight and premature labor in pregnant women.


